Cold and Flu: Key Differences, Symptoms, and Prevention Tips
Understanding Cold and Flu: Key Differences, Symptoms, and Prevention
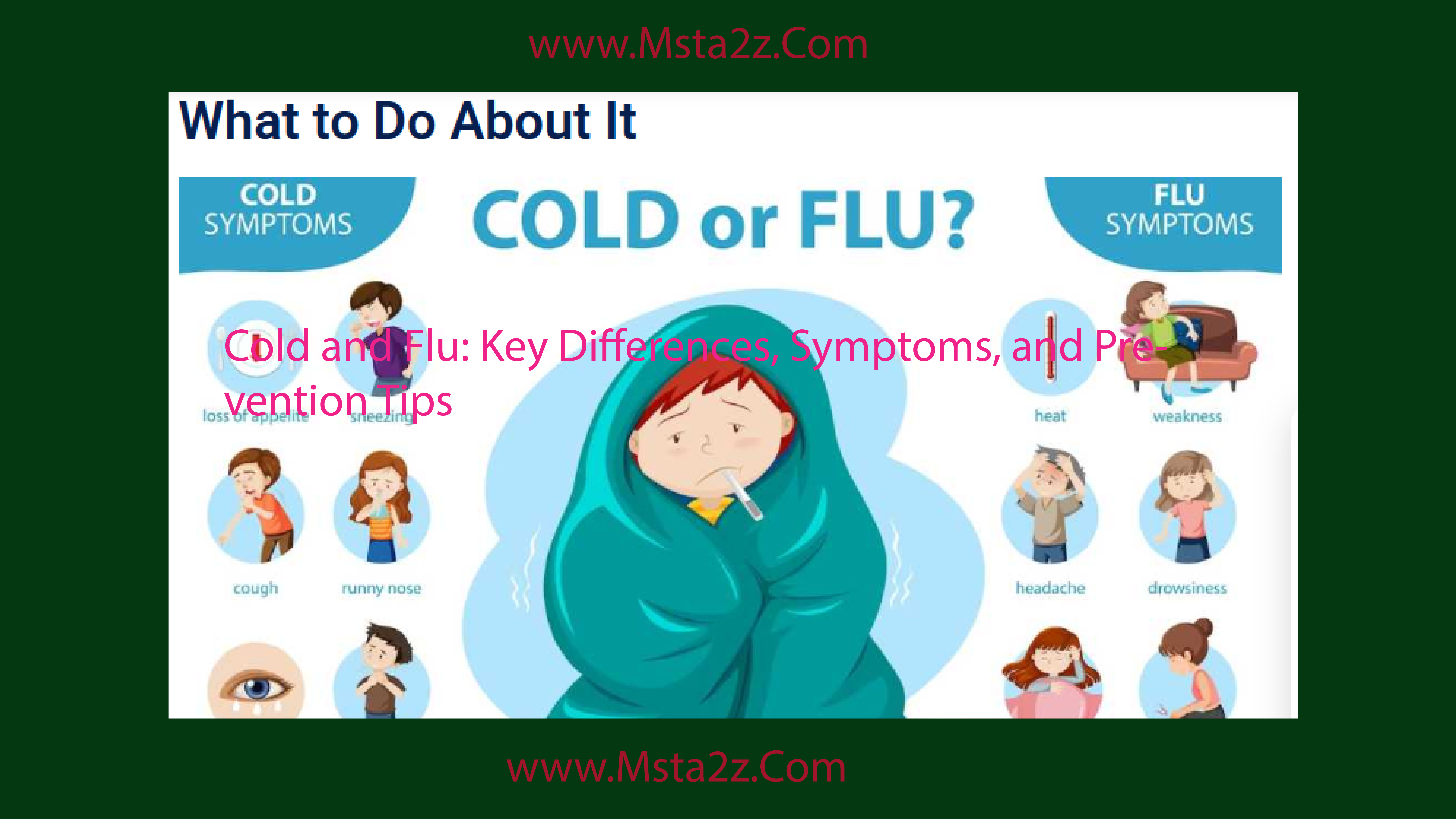
The common cold and the flu are two of the most common illnesses, especially in the fall and winter. Despite their frequent occurrence, many still struggle to differentiate between the two, leading to confusion about symptoms, treatments, and prevention. We’ll talk about what the cold and the flu are, how to tell them apart, what they look like, and how to avoid getting them. #### What is a Cold?
A viral infection that mostly affects the upper respiratory system is known as a cold, or common cold. It is caused by several different viruses, with rhinoviruses being the most common culprit. Colds are highly contagious and can be spread through contact with contaminated surfaces or droplets in the air. The symptoms of a cold typically appear gradually, with mild to moderate effects on the body.
#### What is the Flu?
The flu, or influenza, is also a viral infection but is caused by influenza viruses, which are different from the viruses that cause the common cold. The flu can affect both the upper and lower respiratory systems and tends to be more severe than the common cold. Influenza can lead to complications such as pneumonia, bronchitis, or even hospitalization, especially in vulnerable populations like the elderly, young children, and those with weakened immune systems.
#### Key Differences Between Cold and Flu
While both the cold and the flu share similar symptoms, they can be distinguished based on severity, onset, and accompanying signs.
- Onset of Symptoms:
- Cold: Symptoms usually appear gradually over a few days.
- Flu: Symptoms come on suddenly and can intensify quickly.
- Fever:
- Cold: Rarely causes fever. When it does occur, it’s usually low-grade.
- Flu: Fever is common, and it can be high (above 100°F or 37.8°C).
- Body Aches:
- Cold: Any mild body aches that may exist – Flu: Severe body aches, headaches, and muscle pain are common.
- Fatigue:
- Cold: Mild exhaustion, but most people are able to function. – Flu: Extreme fatigue, which can last for several days.
- Cough:
- Cold: Mild to moderate cough, often a dry or productive one.
- Flu: A dry, persistent cough that can be severe.
- Nasal Congestion and Sneezing:
- Cold: Frequent nasal congestion, sneezing, and sore throat.
- Flu: Nasal symptoms are less prominent compared to the cold. However, a sore throat can still occur.
- Duration:
- Cold: Typically lasts 7-10 days.
- Flu: Can last anywhere from a few days to two weeks, with severe symptoms lasting the longest.
#### How to Prevent Cold and Flu
Prevention is always better than treatment, especially with illnesses that spread quickly in communities. Here are several steps you can take to minimize your chances of contracting the cold or flu:
- Get vaccinated: The flu vaccine is one of the most effective ways to prevent influenza. If you do get the flu, it significantly reduces the severity and complications. However, it does not guarantee that you will not contract it. Annual vaccination is recommended, especially for those at high risk.
- Wash Hands Regularly:
Regular handwashing is one of the simplest and most effective ways to prevent the spread of germs. Wash your hands with soap and water for at least 20 seconds, especially after coughing, sneezing, or touching common surfaces. - Cover Your Mouth and Nose:
Always cover your mouth and nose with a tissue or your elbow when coughing or sneezing to prevent droplets from spreading. Dispose of used tissues immediately. - Avoid Close Contact:
If someone is sick, try to avoid close contact with them. In busy areas or during peak flu season, consider wearing a mask to protect yourself from airborne viruses. - Maintain a healthy way of life: Eating a balanced diet, getting enough sleep, and exercising regularly can help boost your immune system, making it easier to fend off infections.
- Disinfect Common Surfaces:
Cold and flu viruses can survive on surfaces for hours. Disinfecting commonly touched items like doorknobs, light switches, remote controls, and phones can reduce the risk of infection. - Stay Home if Sick:
If you’re feeling unwell, it’s crucial to stay home, especially during flu season. This allows your body to rest and recover more quickly while also preventing the spread of germs. #### Treating Cold and Flu
While there is no cure for either the common cold or the flu, there are ways to manage symptoms and feel better:
- Cold: Cold symptoms can be alleviated by taking over-the-counter (OTC) medications like decongestants, cough suppressants, or antihistamines. Rest, staying hydrated, and using saline nasal sprays or humidifiers can also help relieve discomfort.
- Flu: For the flu, antiviral medications prescribed by a doctor (like Tamiflu) can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms if taken within the first 48 hours of illness. Rest, hydration, and pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can also help reduce fever and aches.
It’s important to consult a healthcare provider for both conditions if symptoms worsen or if you fall into a high-risk category for complications.
#### Conclusion
Both the cold and the flu are common viral illnesses, but they differ in their severity and symptoms. The flu can lead to more serious health issues, whereas the common cold is typically mild. Prevention through vaccines, proper hygiene, and healthy lifestyle choices is key to avoiding these illnesses. If you do catch a cold or the flu, managing your symptoms properly can help you recover faster and avoid complications. Always remember that if you’re unsure about your symptoms or how to treat them, seeking medical advice is always a good idea.